Algorithms have a long history, and the word can be traced back to the 9th century. At this time, the Persian mathematician Abdullah Muhammad bin Musa al-Khwarizmi often cited as "The father of Algebra," was indirectly responsible for creating the term "Algorithm." In the 12th century, one of his books was translated into Latin, where his name was rendered in Latin as "Algorithmi." But this was not the beginning of algorithms! The idea of an algorithm existed before. Let's have a look:
- Two thousand years back, Euclid designed an algorithm for finding the GCD of two numbers.
- Vedic mathematicians used the Urdhva Tiryakbhyam algorithm for fast integer multiplication.
- Babylonians and Egyptians used arithmetic algorithms, such as a division algorithm.
- Greek mathematicians used Sieve of Eratosthenes algorithms for finding prime numbers.
- Arabic mathematicians used cryptographic algorithms for code-breaking.
- Chinese mathematicians discovered the Chinese Remainder Theorem in the 3rd century AD.
- The Babylonian-Sumerian method of extracting a root was one of the first documented examples of mathematical algorithms.
- Gauss developed the Gaussian elimination algorithm for solving a system of linear equations.
- Brahmagupta, Bhaskara, and Jayadeva designed the "Chakravala" method, a cyclic algorithm to solve indeterminate quadratic equations.
Even most of the above algorithms are still relevant. Now the critical question is - Why we used the above algorithms in ancient times? Are algorithms just about computers or more than that? Think!
Timeline of famous algorithms after 1500 AD
- 1540 — method to find the roots of a quartic polynomial
- 1545 — method for finding the roots of a cubic polynomial
- 1614 — method for performing calculations using logarithms
- 1671 — Newton–Raphson method
- 1842 — The first algorithm for a computing engine
- 1847—George Boole unified logic with calculations and formed the basis of today's computing logic: Boolean Algebra.
- 1888— Giuseppe Peano established the axiomatisation of mathematics. He used equations with symbols to obtain results that would later become rules that modern-day mathematics and algorithms are based on.
- 1930 — Lambda calculus. It is equivalent to a Turing machine that has provided a solid theoretical foundation for functional programming languages.
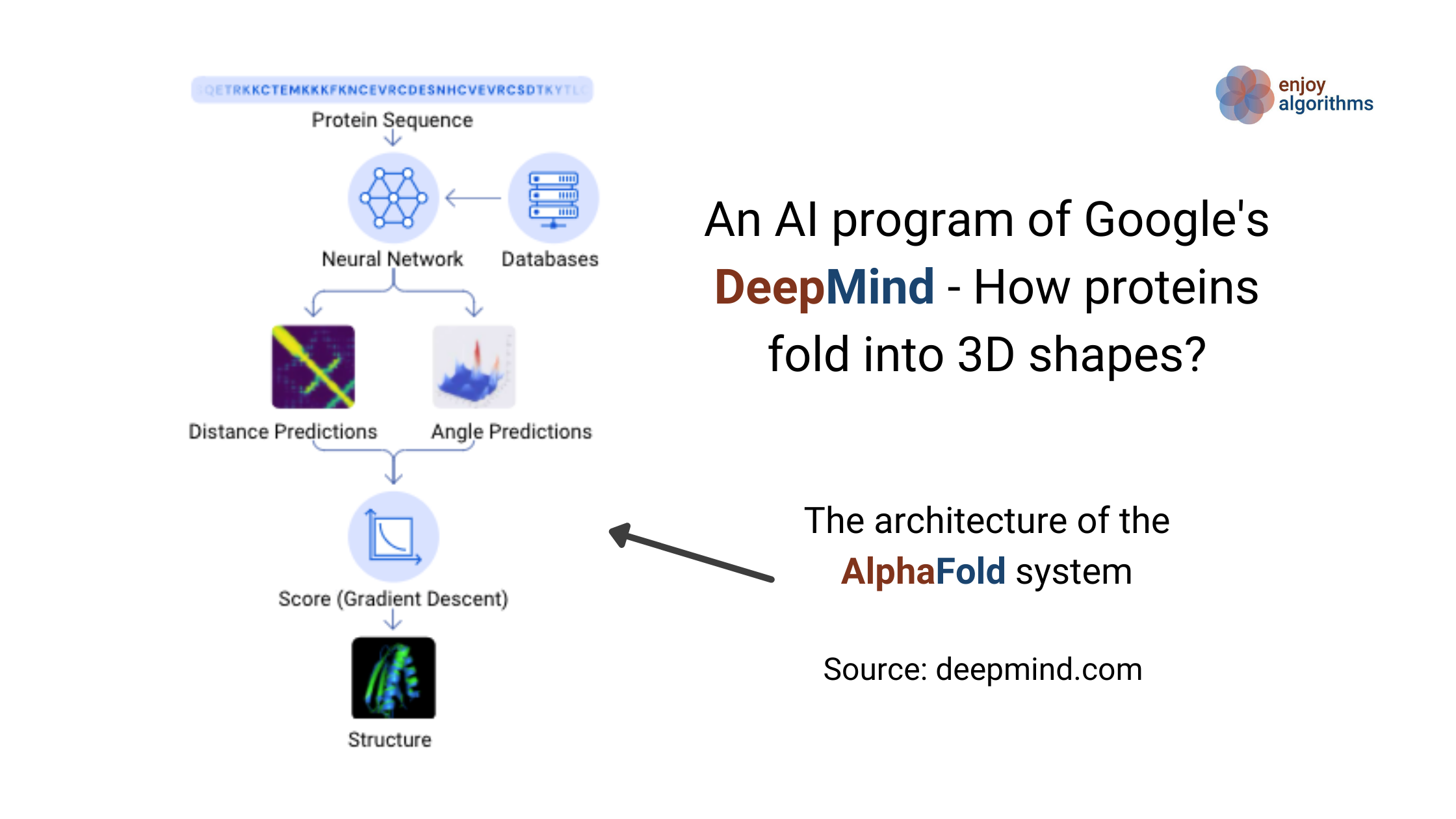
- 1936 — Turing machine, an abstract machine that developed the modern notion of "algorithm."
- 1942 — A fast Fourier transform algorithm
- 1945 — Merge sort
- 1943—Kleene's algorithm. It transforms a given nondeterministic finite automaton into a regular expression.
- 1947 — Simplex algorithm
- 1952 — Huffman coding
- 1954 — Radix sort algorithm
- 1956 — Kruskal's algorithm
- 1956 — Ford–Fulkerson algorithm
- 1957 — Prim's algorithm
- 1957 — Bellman-Ford algorithm
- 1959 — Dijkstra's algorithm
- 1959 — Shell sort
- 1960 — Karatsuba multiplication
- 1962 — AVL trees
- 1962 — Quicksort
- 1962 — Stable-marriage algorithm
- 1964 — Heapsort
- 1965 — Cooley–Tukey algorithm
- 1965 — Levenshtein distance
- 1965 — LR parsers
- 1967 — Viterbi algorithm
- 1968 — A* graph search algorithm
- 1969 — Strassen algorithm for matrix multiplication
- 1972 — Graham scan
- 1972 — Red-black trees and B-trees
- 1973 — RSA encryption algorithm
- 1973 — Jarvis march algorithm
- 1973 — Hopcroft–Karp algorithm
- 1974 — Quadtree developed
- 1976 — Knuth–Morris–Pratt algorithm
- 1977 — Boyer–Moore string search algorithm for searching the occurrence of a string into another string.
- 1980 — Brent's Algorithm for cycle detection
- 1983 — Classification and regression tree algorithm
- 1984 — Karmarkar's interior-point algorithm
- 1985 — Splay trees
- 1986 — Push relabel maximum flow algorithm
- 1991 — Wait-free synchronization
- 1993 — Apriori algorithm
- 1993 — Algorithm to compute the minimum cut of a connected graph
- 1998 — PageRank algorithm
- 2001 — Distributed hash table
- 2001 — BitTorrent, the first fully decentralized peer-to-peer file distribution system, is published
- 2009 — Bitcoin, a first trust-less decentralized cryptocurrency system, is published
Conclusion
Now with increasing computing power, algorithms have grown in their level of complexity. The present generation is moving towards artificial intelligence and quantum computing. We are on the verge of a time where 'bots' or 'robots' are looking to replace our daily activity. Algorithms are evolving at every stage of technological innovation while keeping the basis of operations constant from ancient times. Algorithms are present in every generation in different forms. Nowadays, it is everywhere. Enjoy Algorithms!